CPC Ingredients - Natural Colorants With Added Benefits
Increasingly, consumers are demanding all-natural cosmetics. As a result, more manufacturers are seeking natural coloring materials for all types of products-including foundation, lip care products, and hair coloring. Several natural colorants in use today have a long history of use in foods and cosmetics. Many are plant pigments or dyes with a history of safe use for humans.
Increasingly, consumers are demanding all-natural cosmetics. As a result, more manufacturers are seeking natural coloring materials for all types of products-including foundation, lip care products, and hair coloring.
Several natural colorants in use today have a long history of use in foods and cosmetics. Many are plant pigments or dyes with a history of safe use for humans.
Many of these plant extracts also provide multifunctional benefits that go far beyond their coloring properties alone. For instance, plant pigments such as anthocyanins and carotenoids have scientifically validated antioxidant and antiinflammatory benefits. Historically, curcumin, beet anthocyanins, carotenoids from peppers and saffron, and chlorophyll from green leaves have been used to color food and cosmetics for centuries. Below are a few natural colorants that can provide a range of added benefits, including UV protection and healthy antiaging skin support.
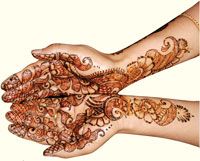
Henna
Henna, also known as Lawsonia alba or Lawsonia inermis, has been used as a coloring and cosmetic agent for more than three thousand years. Its most popular, contemporary use in temporary tattoos stems from its traditional application in the Middle East for decorating the soles of the feet and the palms of the hands.
By itself, henna's active principle, lawsone, is colorless. However, when exposed to sunlight or to air, lawsone is converted into a new compound that provides henna's characteristic red color. Lawsone has been widely used in cosmetology for its dying properties for hair and nail coloring.
Misconceptions regarding the safety of henna are based on reports involving what is known as "black henna." Black henna contains additives such as para-phenylenediamine (PPD) and other related chemicals. Typically, these chemicals are added to natural henna to enrich its color by creating a black hue or to shorten henna-application times. Individuals who are deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) are reportedly adversely affected by topical exposure to PPD and related compounds. Therefore, commercial henna, unless adequately characterized, should be avoided by young children and also by individuals who are known to be G6PD-deficient, to prevent accidental exposure to henna-PPD mixtures.
Other than the cases described above, natural henna and its active component lawsone do not normally cause adverse reactions.
Lawsone can be used as a hair dye in the acidic pH range of approximately 5.5. When lawsone is blended with Indigofera tinctoria, the hair dye can impart color in various shades ranging from brown to black. Blending lawsone with rhubarb, calendula, chamomile, and other herbs produces various shades of red hair dyes.
In addition to coloring, lawsone can provide multifunctional benefits. For instance, in hair care, it can have antimicrobial and conditioning effects. It can also fight hair loss. For this reason, it can be used to manage alopecia.

Sappanwood Extract
Sappanwood is a type of Brazilwood that is related to legumes found in Southeast Asia and the Malay archipelago. The plant has many uses. It has medicinal abilities as an antibacterial and for its anticoagulant properties. It also produces a reddish dye called brazilin, which can be used to dye fabrics or as a cosmetic colorant.
Brazilin's color ranges from yellow to red, depending on a formula's pH. It lends bright color and aesthetic value to bath soaps and color cosmetics. The property of color change, depending on pH, from yellow to red can be used advantageously to produce "color-changing" lipsticks and other color cosmetics.
Brazilin offers antiinflammatory benefits that are useful in formulations to support sun care and healthy aging. Brazilin also has antimicrobial effects and therefore "immunocosmetic" potential. On account of its strong antibacterial action, Sappanwood extract can be incorporated to preserve the integrity of formulations and used in cosmetic creams, gels, and lotions to provide antibacterial benefits.
Red Sandalwood Extract
Red sandalwood extract is used as an ingredient in ayurvedic medicine to support the management of inflammatory conditions, facilitate wound healing, and improve skin health. The principal red pigments in red sandal heartwood are santalin A and B. These are soluble in organic solvents and in alkaline medium, and have established safety and stability profiles.
The extract can be used as a natural color in various nutricosmetic and cosmetic preparations with the added benefit of antioxidant and antiaging potential. Because this extract is stable in alkaline medium, it can be conveniently used in soaps for its gorgeous deep purplish-rose color. Red sandalwood extract can be added to lipstick and color cosmetic compositions to impart color.
When included in traditional cosmetic formulations with turmeric, red sandalwood imparts a healthy glow to the skin. The powdered heartwood has a pleasant aroma and an attractive red color. It has a history of traditional use in talcum powders.
Red sandalwood can also be ground to a paste with water or honey and applied topically to help lighten post-acne and other facial scars. Ayurvedic literature also describes the "cooling" properties of raktha chandana.
Dr. Lakshmi Prakash is vice president of innovation and business development for ingredient supplier Sabinsa Corp. (Piscataway, NJ).

